Revolutionary Technology: 6G
The focus of network evolution has shifted from human communication (2G, 3G) to data consumption (4G), the internet of things, and industrial automation (5G). 6G, using AI and cognitive technologies, will merge the digital, physical, and human worlds through intelligent knowledge systems and robust computation, creating extrasensory experiences. 6G will be characterized by ultra-high speed, low latency, advanced spectrum utilization, intelligent network management and enhanced security and privacy, enabling applications like immersive VR and AR, autonomous systems, smart cities, and telemedicine (Larsson et al., 2025).
Designing 6G networks is complex, requiring global agreement on technological standards. While 6G standards are still undefined, research is underway through groups like the European Hexa-X, North America’s Next G Alliance, and China’s IMT-2030 Promotion Group. The 6G Industry Association (6GIA) represents Europe’s efforts in this field. In June 2023, the ITU-R introduced the Draft IMT-2030 Framework, outlining 6G usage scenarios, capabilities, and roadmaps. The World Radio Communication Conference in November 2023 set spectrum foundations and the technical specification discussions are expected to begin in 2025, with the first 6G standard in 3GPP Release 21 by 2028 and commercial deployments around 2030 (What’s the Latest on 6G? Standards, Features, Use Cases and Timeline, 2023).
6G Potential and Obstacles
6G aims to achieve 1 Tbps data rate by using THz frequency band, but faces challenges due to limited bandwidth and trade-off between spectral efficiency and SNR. Samsung’s prototype reached 120m distance with 2.3 Gbps, while others achieved higher data rates but with limited range. To improve 6G, new designs using appropriate semiconductors, low-loss materials, and tight RF-antenna integration are needed, along with strategies for network deployment using technologies like RIS to create smart EM environments. (Welcome to 6GWorld, 2024).
The potential impact of 6G technology on daily life
The internet of senses and 6G will change many aspects of our lives. According to IEEE, here are some potential use cases:
- Communication: Holographic meetings could replace conference calls; phones could replace keys and wallets; voice or movement could replace typing.
- Connectivity: 6G could reach remote locations without internet access; humans could communicate better with robots, wearables, and IoT devices.
- Healthcare: Wearables, telesurgery, and implanted sensors could transform healthcare.
- Other industries: Education will be more immersive and reach further; smart agriculture could control water, monitor livestock, and provide accurate pesticide use; 6G smart grids could optimize energy distribution; robots and drones could replace humans for dangerous jobs; sensing where devices are could improve identity and reduce fraud (Nokia, 2023).
6G technology: Patent dynamics and top players
In Questel Orbit, 29,922 patented inventions in 6G technology are analysed, with 57% owned by the top 10 players. Notably, 5,109 are standard-essential patents (SEPs), with minimal litigation and licensing activity. Moreover, 20% of total patents are granted and 74% are pending applications.
- Application Dynamics (Patent Family data)
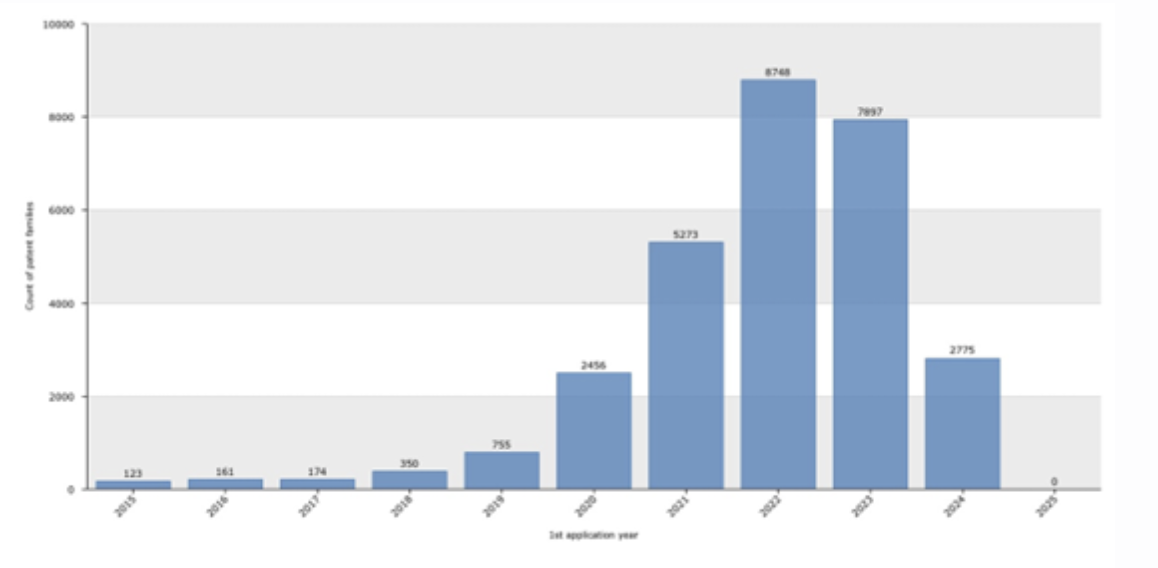
Source : Questel Orbit
The graph above shows the evolution of applications over time, indicating the dynamics of inventiveness of the portfolio studied. The rapid growth of patent families, reaching 8,748 in 2022, 7,897 in 2023, and 2,775 in 2024, signals the emergence of 6G technology.
- Key Players
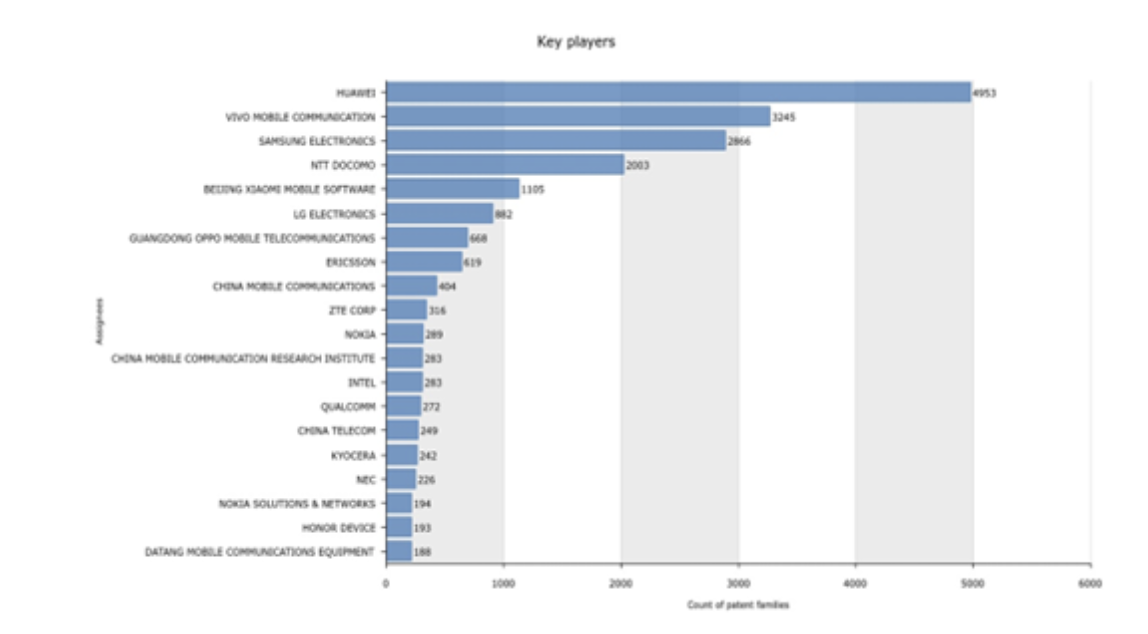
Source : Questel Orbit
The chart below shows the size of the applicants’ portfolios in the patent pool analyzed. This data is a good indicator of the level of inventiveness of the active players.
HUAWEI, VIVO MOBILE communications and SAMSUNG, are leading the way with approximately 36% of all identified inventions, which aligns with the company’s significant 6G research efforts. NTT DOCOMO, ERICSSON, ZTE CORP, and LG ELECTRONICS are also key players, contributing approximately 6%, 2%,1.5%, and 3% of innovation activities, respectively. This confirms their position among the top 10 players in 6G activities.
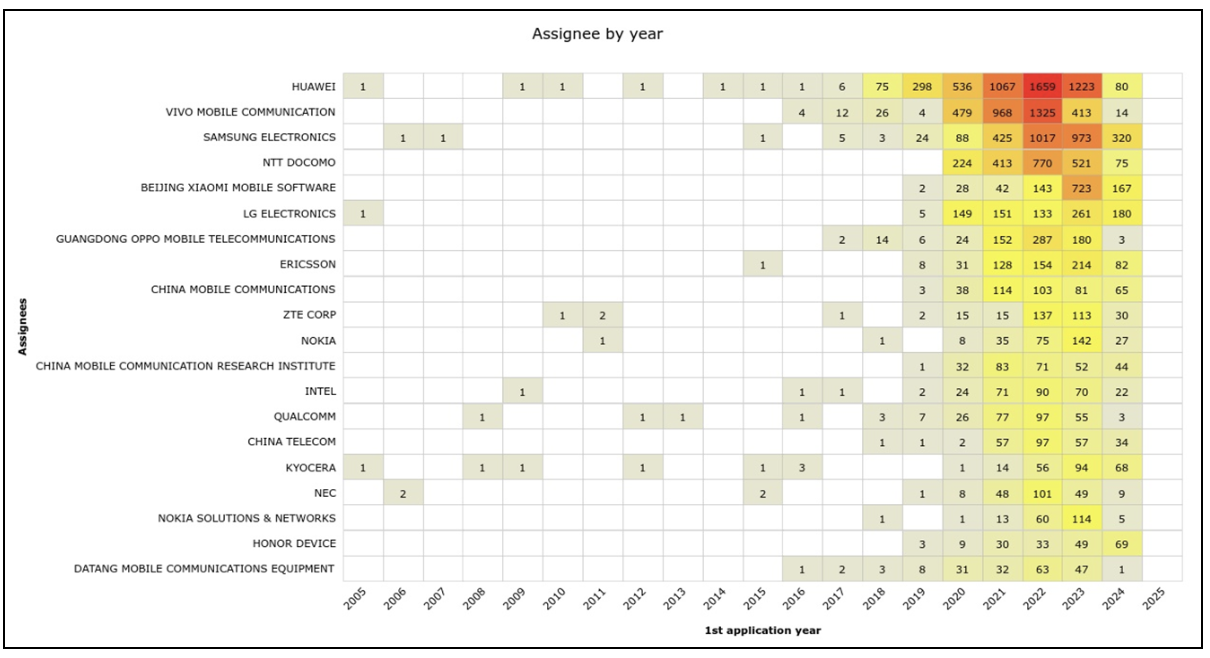
Source : Questel Orbit
This graph highlights patent filing trends by major key players in 6G technology over the years. Huawei dominates, with a sharp increase in patents from 2017, peaking between 2019 to 2023. Samsung Electronics follows with steady filings, particularly from 2017–2023. Vivo, ZTE, and Oppo show growing activity post-2015, while companies like Nokia, Ericsson, and Intel maintain consistent but lower volumes. Emerging players have started contributing in recent years, though at smaller scales. The graph underscores Huawei’s leadership and overall innovation trends in 6G technology in telecommunications.
- Geographical hotspots for 6G Technology.
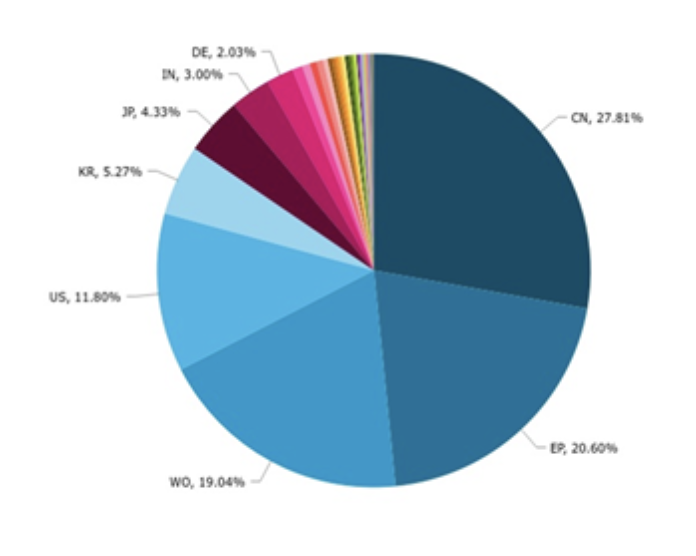
Source : Questel Orbit
China is the leading country of origin for 6G technology inventions, contributing approximately 27.1% of the total identified inventions, while Europe contributes 20.60% and the US 11.80%. While US and Korea contributions to 6G research remain comparatively small compared to those of China and Europe. The relatively high number of Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT) applications (via WIPO) reflects a global protection strategy for a technology that will presumably be essential in enabling the use of 6G technology.

Source : Questel Orbit
This graph illustrates the number of patents related to 6G technology that different countries have published over time. China has taken a commanding lead, with a significant surge in patent publications since 2020. The World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) also holds a substantial number of international patents, demonstrating a steady growth since 2019. The United States maintains consistent activity, while Europe’s contributions remain moderate. South Korea and Japan show steady publication rates but lag behind China and the US. India and Taiwan have emerged as new contributors, particularly from 2020 onwards. Overall, China and WIPO are at the forefront of 6G patent publications, reflecting a strong global effort in advancing this technology.
Although 6G development faces challenges, it has the potential to revolutionize our lives and work. Despite being years away, 6G’s benefits make it a worthwhile investment and likely essential for future global connectivity.
References
- What’s the latest on 6G? Standards, features, use cases and timeline. (2023, September 7). Thales Group. https://www.thalesgroup.com/en/worldwide/digital-identity-and-security/magazine/whats-latest-6g-standards-features-use-cases-and
- Larsson, D. C., Grövlen, A., Parkvall, S., & Liberg, O. (2025, January 3). 6G standardization – an overview of timeline and high-level technology principles. ericsson.com. https://www.ericsson.com/en/blog/2024/3/6g-standardization-timeline-and-technology-principles
- Welcome to 6GWorld. (2024, May 14). 6G 101: What is 6G technology and how it works. https://www.6gworld.com/blog/what-is-6g-technology-and-how-it-works/
- Nokia. (2023, August 11). 6G explained. Nokia.com. https://www.nokia.com/about-us/newsroom/articles/6g-explained/
Our Partners